Goodrich plant near louisville kentucky were diagnosed with liver angiosarcoma also known as hemangiosarcoma a.
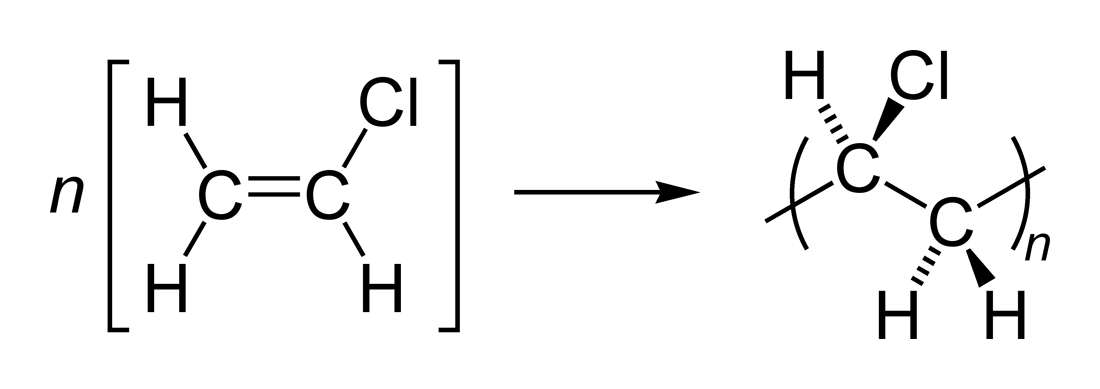
Vinyl chloride polymerization reaction.
Vinyl acetate is an industrial chemical that is produced in large amounts in the united states.
Physical phenomena of polyvinylchloride parti cle formation and reactant species distributions in phas s during poly merization.
Specifically workers in polymerization section of a b f.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced in an addition polymerisation reaction using the chloroethene vinyl chloride monomer.
All elementary reactions occurring during the vcm free radical polymerization were grouped into five reaction families consisting of forward and backward steps cfr figure 2.
Vinyl acetate is used to make other industrial chemicals.
To achieve this the free radical polymerization of vinyl chloride was modeled at the elementary reaction level.
Vinyl chloride is an organochloride with the formula h 2 c chcl that is also called vinyl chloride monomer vcm or chloroethene this colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride pvc.
Polyvinyl chloride is a white rigid quite brittle solid.
Suspension and emulsion polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer using free radical initiators.
Vinyl chloride is an organohalogen compound that has important industrial applications.
In the early 1970s the carcinogenicity of vinyl chloride usually called vinyl chloride monomer or vcm was linked to cancers in workers in the polyvinyl chloride industry.
It is a clear colorless liquid with a sweet fruity smell.
When treated with certain catalysts vinyl chloride monomers undergo polymerization and form the larger compound known as polyvinyl chloride or pvc.
It is a carcinogenic gas that must be handled with special protective procedures.
This polymerisation reaction proceeds by a free radical mechanism.
Vinyl chloride ch 2 chcl is most often obtained by reacting ethylene with oxygen and hydrogen chloride over a copper catalyst.
About 13 billion kilograms are produced annually.
A comprehensive reactor model for batch and semi batch proc esses has been developed on the basis of these.
Pvc is used in the manufacture of numerous products including packaging films and water pipes.
It is very flammable and may be ignited by heat sparks or flames.
Foaming above the aqueous polymerization mixture can be efficiently reduced in suspension polymerization of vinyl chloride monomer in an aqueous medium contained in a polymerization reactor equipped with a reflux condenser for removal of the heat of polymerization by admixing the polymerization mixture with additives comprising a from 0 002 to 0 007 part by weight of a partially saponified.
Vinyl chloride is a chlorinated hydrocarbon occurring as a colorless highly flammable gas with a mild sweet odor that may emit toxic fumes of carbon dioxide carbon monoxide hydrogen chloride and phosgene when heated to decomposition.